DNA Datasets: The Future of Biotechnology and the Critical Role of Synthetic Data (10/18)
Table of Contents

As generative AI breaks new ground in various fields, its potential to revolutionize biology through the creation of synthetic DNA datasets is particularly exciting. What once seemed like science fiction—using AI to generate DNA sequences—is now a powerful reality, opening new avenues in research, medicine, and biotechnology. This innovation in DNA data synthesis brings significant ethical concerns, particularly regarding privacy and data ownership.
The Revolutionary Power of AI-Generated DNA Datasets
Generative AI models, originally developed for natural language processing and image synthesis, are now being adapted to generate biological sequences like DNA, RNA, and proteins. These advanced models analyze vast biological datasets, identify complex patterns, and create novel sequences not found in nature. The emergence of synthetic data not only addresses these issues but is rapidly becoming an essential technology for the future of genomic research and applications. Here’s why this matters:
- Accelerating biological research: Generative models can simulate DNA sequences that behave like real biological data, allowing researchers to explore genetic mutations or develop new gene therapies without needing physical samples.
- Drug discovery and personalized medicine: AI-generated DNA sequences can be used to design personalized treatment options, tailoring therapies to the specific genetic makeup of an individual. This can drastically cut down the time and cost of developing new drugs.
- Environmental and agricultural innovation: Beyond human health, generative AI can create DNA sequences that help develop resilient crops or even new forms of sustainable energy.

Ethical Dilemma: Privacy Concerns in the Age of AI
While the ability of AI to generate biological data is exciting, it also brings up serious ethical and privacy concerns. DNA is not just a sequence of nucleotides—it’s deeply personal and identifies everything about an individual. If AI can create DNA sequences similar to real ones, it could potentially lead to data breaches, identity theft, or misuse of sensitive information.
- Data privacy and ownership: Who owns the synthetic DNA created by AI? If this synthetic data closely resembles real genetic information, can it be considered private?
- Potential for misuse: AI-generated DNA could be used for malicious purposes, including biohacking or unauthorized genetic experiments, raising the stakes in bioethics and cybersecurity.
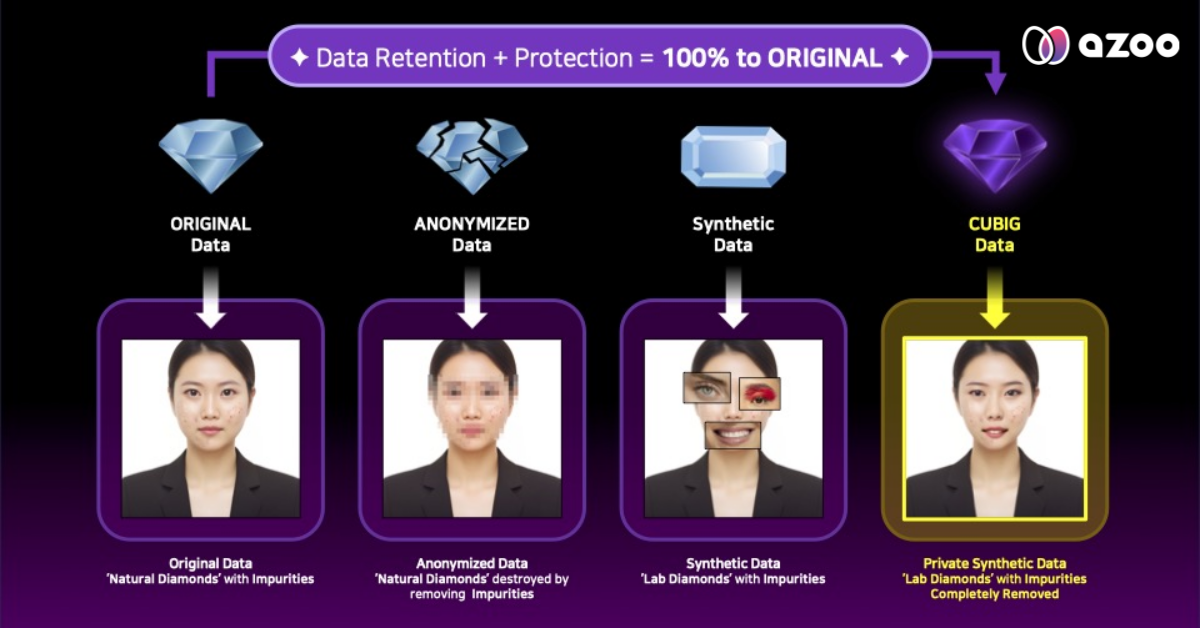
Why Synthetic Data is an Unstoppable Force
The immense potential and significant risks associated with AI-generated DNA make synthetic data not just a temporary solution, but a necessity in the era of advanced AI. Here’s why:
- Scalability: AI models require vast datasets to function optimally. Synthetic data can be generated in virtually unlimited quantities, facilitating breakthroughs in genomics and personalized medicine.
- Cost-efficiency: Collecting and sequencing real biological data is both expensive and time-consuming. Synthetic data offers a faster, more affordable alternative without compromising research quality.
- Ethical compliance: Synthetic data helps ensure that innovations in biotechnology and genomics align with ethical standards. It protects individual privacy while enabling progress in a safe, controlled manner.

Secure Synthetic Data: The Solution We Can’t Ignore
The power to generate DNA brings with it the responsibility to manage data ethically. Secure synthetic DNA datasets—AI-generated DNA datasets that mimics real-world data with enhanced security measures—offers a compelling solution to both innovation and ethical concerns. By simulating realistic data without using actual genetic information, secure synthetic data provides several key advantages:
- Privacy by design: Synthetic data ensures that no real genetic information is exposed or compromised. Researchers can work with data that behaves like the real thing but has no link to any actual person.
- Expanding datasets without ethical risk: Using synthetic DNA, scientists can vastly increase the size of datasets they work with, which is crucial for training models in the biomedical field. This reduces dependency on actual human samples, mitigating risks tied to consent, privacy, and ownership.
- Faster, safer innovation: With synthetic data, AI systems can generate new possibilities faster, safely accelerating research and development in biotech, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare.
